Understanding Phishing Attacks: 7 Tips to Spot and Avoid Them
In today’s digital age, phishing attacks have become one of the most prevalent and dangerous threats to both individuals and businesses. These deceptive schemes often trick people into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or even social security numbers. Understanding what phishing is and knowing how to spot and avoid these attacks can save you from significant financial loss and identity theft.
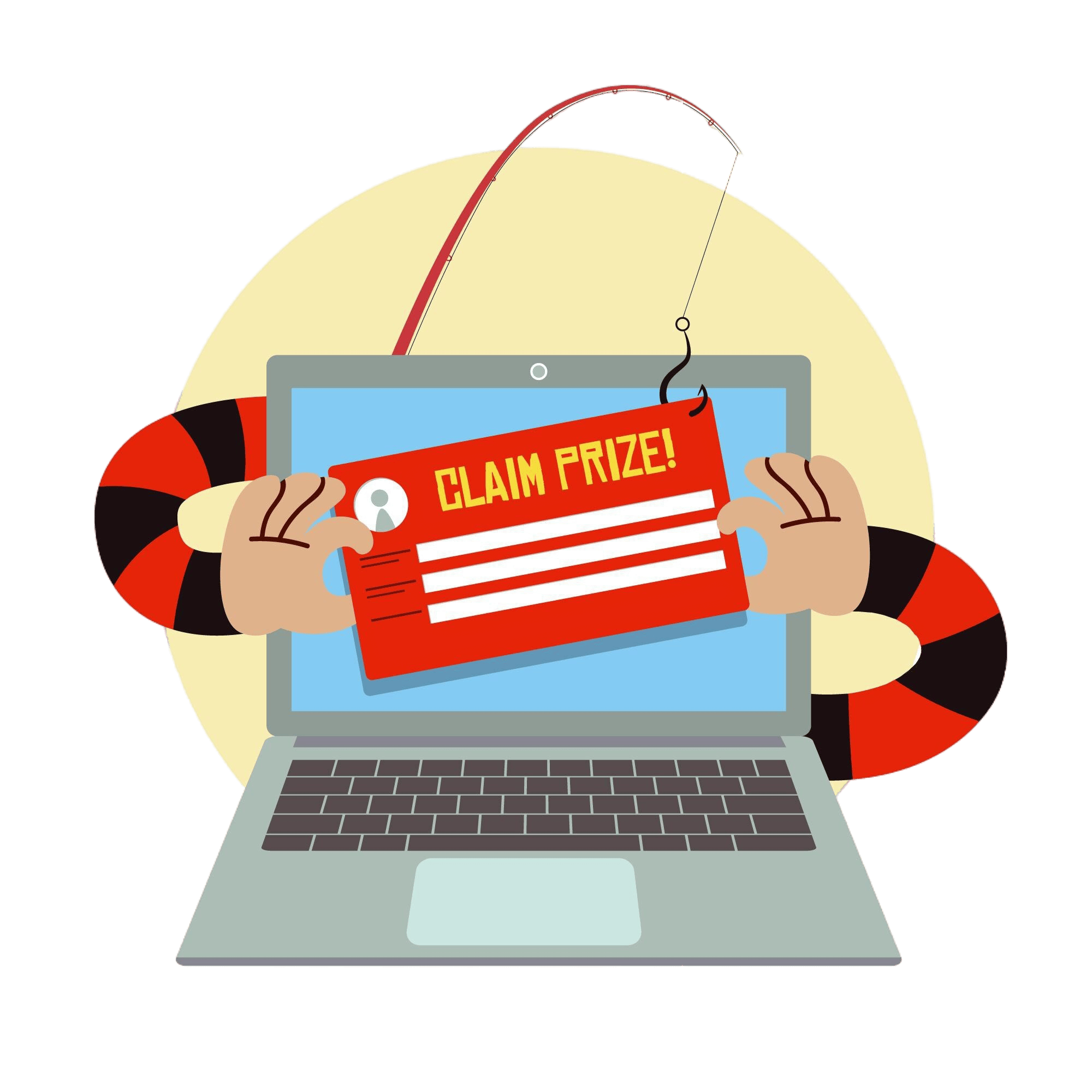

What is Phishing Attacks?
Phishing is a type of cyber attack where attackers disguise themselves as trustworthy entities to steal sensitive information. These attacks often come in the form of emails, text messages, or fake websites that appear legitimate but are designed to trick you into providing personal information.
Common Types of Phishing Attacks
- Email Phishing: The most common form, where attackers send emails that seem to be from a trusted source like your bank, social media site, or even a coworker. The email typically contains a link that directs you to a fake website designed to steal your login credentials or financial information.
- Spear Phishing: Unlike general phishing attacks, spear phishing is targeted. Attackers tailor their approach to a specific individual or organization, often using information from social media to make the email appear more legitimate.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): In smishing, attackers send text messages pretending to be from reputable companies or contacts, urging the victim to click on a link or call a number where they will be asked to provide personal information.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Vishing involves phone calls from attackers who impersonate representatives from banks, government agencies, or tech support to obtain sensitive information.
- Clone Phishing: In this method, a legitimate, previously delivered email is copied and slightly altered to include malicious links or attachments. The modified email is then sent from a spoofed address, making it look like a genuine follow-up.
How to Spot a Phishing Attacks
Recognizing the signs of a phishing attempt is crucial in protecting yourself:
- Suspicious Sender: Always check the sender’s email address. Phishing emails often come from addresses that are similar but not identical to legitimate ones.
- Urgency and Fear Tactics: Be wary of messages that create a sense of urgency, like threats to close your account or warnings about suspicious activity.
- Unexpected Attachments or Links: If you receive an unexpected attachment or are asked to click on a link, it’s best to verify the legitimacy before taking any action.
- Misspellings and Poor Grammar: Many phishing emails contain spelling errors or awkward phrasing that wouldn’t be present in a legitimate email.
How to Avoid Phishing Attacks
Here are some practical tips to protect yourself from phishing scams:
- Verify the Source: If you receive an unexpected email or message, contact the organization or individual directly using a trusted method (not by replying to the email or message) to verify its authenticity.
- Hover Over Links: Before clicking on any link, hover your mouse over it to see the actual URL. If the link looks suspicious or doesn’t match the expected destination, don’t click it.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA on your accounts whenever possible. Even if an attacker obtains your password, they’ll need the second form of verification to access your account.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that your operating system, browser, and antivirus software are up to date. Many phishing attempts exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Regularly educate yourself and others about the latest phishing techniques and how to avoid them. Awareness is one of the most powerful tools in combating phishing.
- Be Cautious with Personal Information: Never provide personal information in response to an unsolicited request, whether it’s through email, phone, or text message.
- Report Phishing Attempts: If you receive a phishing email, report it to your email provider, the company being impersonated, or a relevant cybersecurity agency.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks are evolving and becoming more sophisticated, but by staying informed and vigilant, you can protect yourself from falling victim to these scams. Remember, when in doubt, always err on the side of caution. Your personal information is valuable—don’t let it fall into the wrong hands.